What is Data Science ?
“You can have data without information, but you cannot have information without data.” – Daniel Keys Moran
Data science is one of the most debated topics in the industries these days. Its popularity has grown over the years, and companies have started implementing data science techniques to grow their business and increase customer satisfaction. According to a study conducted in 2013, 90% of the world’s data has been produced within the previous two years. In 2020, the global amount of data is projected to reach 59 zettabytes. Given the massive amount of data that is being created every second, people in almost all industries have become concerned as to how to make use of all this data being produced. This is when Data Science comes into play.
What is Data Science ?
Data science is the domain of study that deals with vast volumes of data using modern tools and techniques to find unseen patterns, derive meaningful information, and make business decisions. Data science uses complex machine learning algorithms to build predictive models.
“Data Scientist (n.): Person who is better at statistics than any software engineer and better at software engineering than any statistician.” – Josh Wells
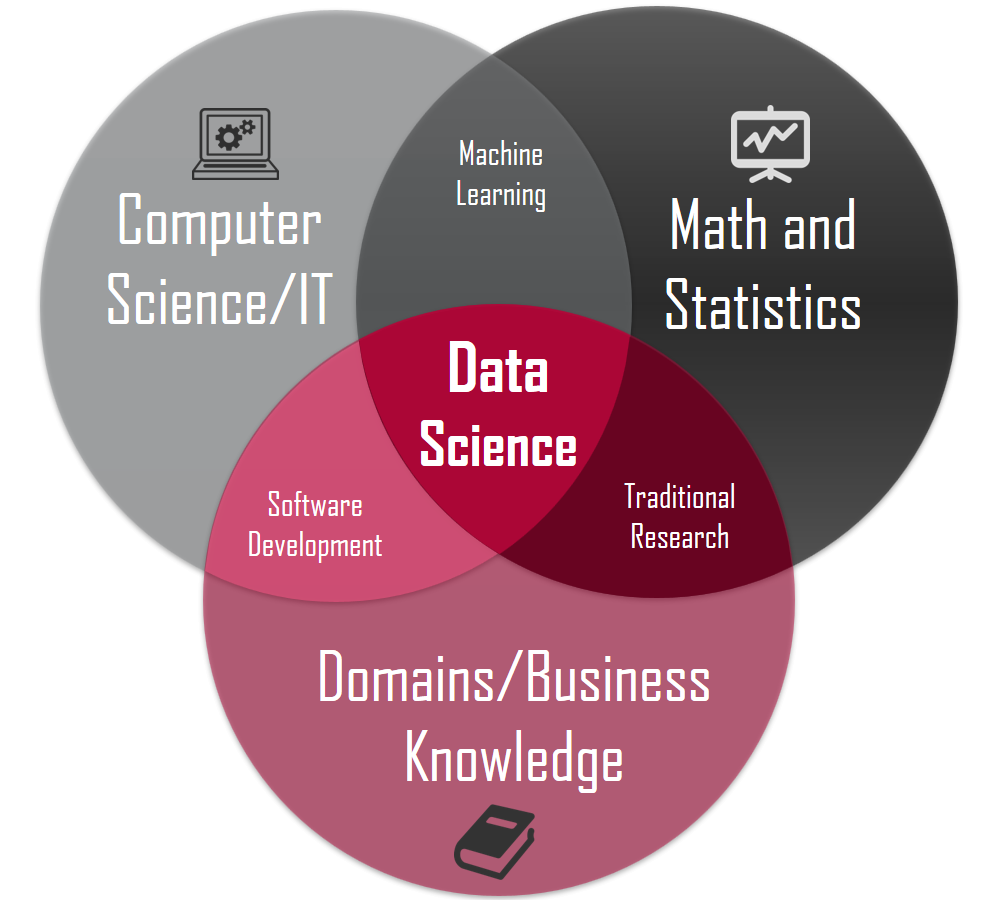
Data science combines the scientific method, math and statistics, specialized programming, advanced analytics, AI, and even storytelling to uncover and explain the business insights buried in data.It envolves preparing raw data to make it ready for processing, performing data analysis, and presenting the results to reveal patterns abd enable stakeholders to extract useful insights.
Data preparation envolves cleaning, aggregating, and manipulating data in a way that makes it suitable for the desired type of processing. As for analysis, it is requires algorithms and AI models to explore the data and extract patterns. Decisions will be taken based on the predictions that have been with the models.
In order for these models to be able to predict reliably, they have to be optimized through training. And the accuracy of the predictions must be validated through scientifically designed tests and experiments.
What are the prerequisites and skills for Data Science ?
a data scientist must be able to do the following tasks :
- Apply mathematics, statistics, and the scientific method
- Use a variety of tools and techniques for evaluating and preparing data (SQL, data mining, data integration methods…)
- Extract insights from data using predictive analytics and artificial intelligence (AI), including machine learning and deep learning models
- Write applications that automate data processing and calculations
- Tell stories that clearly depict the results of the analysis process (this is usually done through visualization and other techniques)
- Explain how these results can be used to solve business problems
Technical prerequisites for Data Science
Here are some technical demands you should know before setting of a data science journey :
Mathematics : data science requires some basic knowledge in certain mathematical concepts such as calculus, linear algebra, probability, statistics, information theory… data scientists should be familiar with these concepts in order to be able to fully understand the magic behind statistical and machine learning models, and thus be capable of adapting them to their needs.
Programming : some programming skills are needed to execute successful data science projects. It is not required to be a hardcore programmer to help analyze widespread parts of data, to write quotes efficiently to explain the problem area and work with big data. Data science works on programming tools like Python and R. These concepts will help the candidate to journey a long way into the expertise of data science.
Databases : they are an essential component of data science. Data scientists need to understand how databases work, how to manage them, and how to extract data from them.
Machine learning : it is one of the most fundamental concepts of data science. Data Scientists need to have a solid grasp on ML in addition to basic knowledge of statistics.
| Field | Skills | Tools |
|---|---|---|
| Data Analysis | R, Python, Statistics | SAS, Jupyter, R Studio, MATLAB, Excel, RapidMiner |
| Data Warehousing | ETL, SQL, Hadoop, Apache Spark | Informatica/ Talend, AWS Redshift |
| Data Visualization | R, Python libraries | Jupyter, Tableau, Cognos, RAW |
| Machine Learning | Python, Algebra, Machine learning algorithms, Statistics | Spark MLib, Mahout, Azure ML studio |

Data Science Lifecycle

Data science projects are conducted through several processes, so it is important to have a general structure to follow. There are no rules or stricts procedures to follow in a data science project. However, the following lifecycle outlines the major stages that projects typically execute, often iteratively:
- Business Understanding : This is the first step of all data science projects. It includes two main tasks :
- Define objectives: Work with your customer and other stakeholders to understand and identify the business problems. Formulate questions that define the business goals that the data science techniques can target.
- Identify data sources: Find the relevant data that helps you answer the questions that define the objectives of the project.
Data Collection : It is not an easy process. It involves so many tasks such as identifying your data requirements, deciding on a method of data collection, and finally organizing a data collection plan that synthesizes the most important aspects of your program.
Data Preparation : This step is also known as Data Cleaning or Data Wrangling. It includes steps like selecting the relevant data, integrating the data by merging the data sets, cleaning it, handling the missing values by either removing them or imputing them with relevant data, treating erroneous data by removing them, also check for outliers and handle them. Constructing new data, derive new features from existing ones by using the feature engineering. Format the data into the desired structure, remove unwanted columns and features. Data preparation is the most time consuming as it takes up to 80% of the overall project time, yet it’s the most important step in the entire life cycle.
Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA) : This is not a formal process with a strict set of rules. It is rather a mindset that incites you to analyze and investigate your data sets and summarize their main characteristics, often employing data visualization methods. It helps you to figure out the best way to manipulate your data. In this stage, you may want to do the following tasks :
- Generate questions about your data
- Search for answers by visualising, transforming, and modelling your data
- Use what you learn to refine your questions and/or generate new questions
Modeling : Data modeling is the process of creating a visual representation of either a whole information system or parts of it to communicate connections between data points and structures. The goal is to illustrate the types of data used and stored within the system, the relationships among these data types, the ways the data can be grouped and organized and its formats and attributes.Data modeling employs standardized schemas and formal techniques. This provides a common, consistent, and predictable way of defining and managing data resources across an organization, or even beyond.
Model Evaluation : In the end we need to evaluate the model by measuring the accuracy (How well the model performs i.e. does it describe the data accurately) and relevance (Does it answer the original question that is set out to answer). We also need to make sure there is a correct balance between performance and generalizability, which means the model created should not be biased and should be a generalized model.
Model Deployment : In order to start using a model for practical decision-making, it needs to be effectively deployed into production. Depending on the requirements, the deployment phase can be as simple as generating a report or as complex as implementing a repeatable data science process. In many cases, it will be the customer, not the data analyst, who will carry out the deployment steps. For example, a credit card company may want to deploy a trained model or set of models (e.g., neural networks, meta-learner) to quickly identify transactions, which have a high probability of being fraudulent. However, even if the analyst will not carry out the deployment effort it is important for the customer to understand up front what actions will need to be carried out in order to actually make use of the created models.
Conclusion
In the end, we won’t be wrong to say that Data Science is driving the future of almost all industries as it is the fastest growing discipline in computer science and IT with all its active community and the new tools being developped continuously.