What is machine learning ?
“What we want is a machine that can learn from experience”
Alan Turing, 1947
What is machine learning ?
Machine learning is a form of artificial intelligence (AI) that allows a system to learn from data without explicitly programming the instructions to be executed. However, machine learning is not a simple process. As the algorithms ingest the training data, it becomes possible to create more accurate models based on that data. A machine learning model is the output generated when you train your machine learning algorithm with data. After training, when you provide input data to a model, you receive an output result. For example, a predictive algorithm creates a predictive model. Then, when you provide data to the predictive model, you receive a forecast that is determined by the data that was used to train the model.
Iterative learning from data
Machine learning allows models to train on datasets before being deployed. Some machine learning models are online and operate continuously. This iterative process of inline models improves the types of associations established between data elements. Due to their complexity and size, these trends and associations may not be detected by a human observer. Once a model has been trained, it can be used in real time to learn from the data. Improvements in accuracy result from the training and automation process that is part of machine learning.
Machine learning approaches
Machine learning techniques are needed to improve the accuracy of predictive models. Depending on the nature of the business problem being addressed, there are different approaches that vary depending on the type and volume of data. In this section, we discuss the categories of machine learning.
Supervised learning
 Supervised learning usually begins with a well-defined data set and some understanding of how that data is classified. The goal of supervised learning is to uncover patterns in data and apply them to an analytical process. These data include characteristics associated with labels that define their meaning. You can, for example, create a machine learning application that can distinguish between millions of animals, based on pictures and written descriptions.
Supervised learning usually begins with a well-defined data set and some understanding of how that data is classified. The goal of supervised learning is to uncover patterns in data and apply them to an analytical process. These data include characteristics associated with labels that define their meaning. You can, for example, create a machine learning application that can distinguish between millions of animals, based on pictures and written descriptions.
Unsupervised learning
 Unsupervised learning is used when the problem requires a massive amount of unlabeled data. For example, social media apps like Twitter, Instagram, and Snapchat all mine very large amounts of untagged data. To understand the meaning of this data, it is necessary to use algorithms that classify the data according to the trends or clusters they detect. Unsupervised learning leads an iterative process, analyzing data without human intervention. It is used with spam detection technology sent by e-mail. Normal emails and spam have too many variables for an analyst to tag spam emails sent in bulk. In contrast, machine learning discriminants, based on clustering and association, are applied to identify unwanted emails.
Unsupervised learning is used when the problem requires a massive amount of unlabeled data. For example, social media apps like Twitter, Instagram, and Snapchat all mine very large amounts of untagged data. To understand the meaning of this data, it is necessary to use algorithms that classify the data according to the trends or clusters they detect. Unsupervised learning leads an iterative process, analyzing data without human intervention. It is used with spam detection technology sent by e-mail. Normal emails and spam have too many variables for an analyst to tag spam emails sent in bulk. In contrast, machine learning discriminants, based on clustering and association, are applied to identify unwanted emails.
Reinforcement learning
 Reinforcement learning is a model of behavioral learning. The algorithm receives feedback from the data analysis and guides the user to the best result. Reinforcement learning differs from other types of supervised learning in that the system is not trained with a sample data set. Instead, the system learns instead through a trial and error method. Therefore, a sequence of successful decisions results in the strengthening of the process, because it is the process that most effectively solves the problem at hand.
Reinforcement learning is a model of behavioral learning. The algorithm receives feedback from the data analysis and guides the user to the best result. Reinforcement learning differs from other types of supervised learning in that the system is not trained with a sample data set. Instead, the system learns instead through a trial and error method. Therefore, a sequence of successful decisions results in the strengthening of the process, because it is the process that most effectively solves the problem at hand.
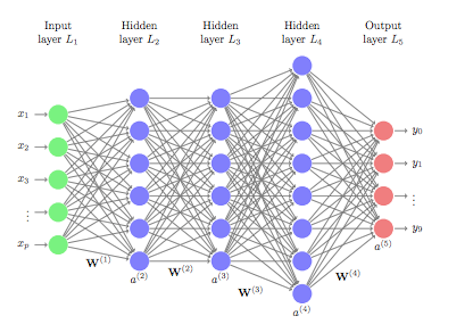
Neural networks and deep learning
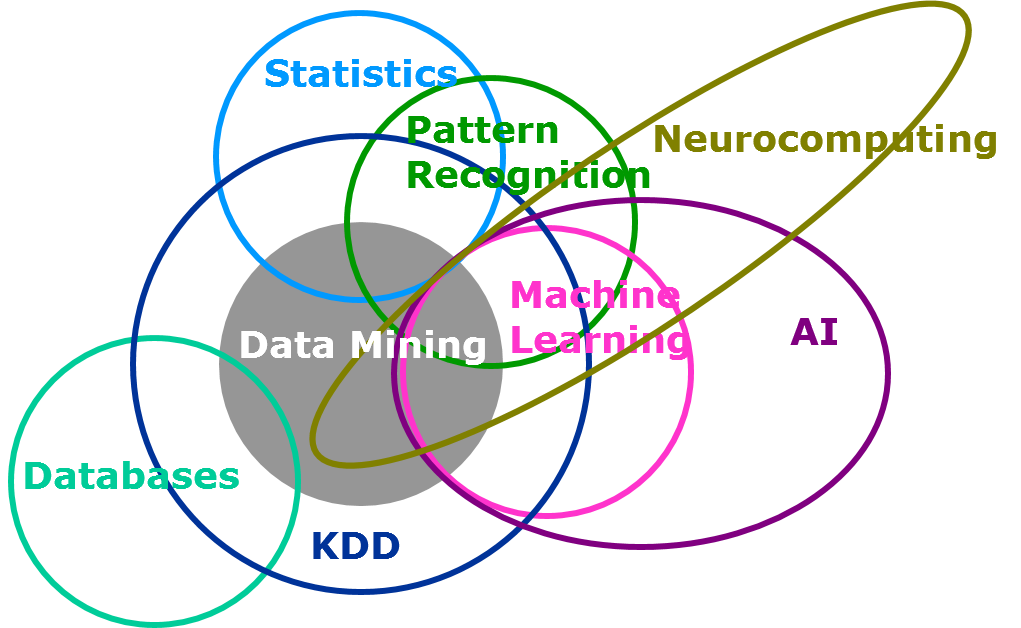
Machine learning vs Statistical Modeling
Statistical modeling and machine learning can be mixed up sometimes. But there is a difference between these two concepts. Machine Learning is an algorithm that can learn from data without being explicitly programmed or relying on standard programming practices. Here are some important facts about machine learning :
- Machine learning is a newer field of study than statistics (machine learning was invented in 1959, whereas statistics originated in the 17th century)
- Machine learning can result in more detailed information than statisticl modeling
- Machine learning is a subfield of computer science and A.I and contributes to building systems that can learn from data without explicit programming
- Finally, machine learning uses fewer assumptions than statistcal modeling
Statistical Modeling is the formalization of relationships between variables in the form of mathematical equations. It is a subfield of math that deals with finding relationships between variables to predict outcomes. It deals with a small amount of data with fewer attributes and, as such, there is a good chance that over-fitting will occur.
Statistical modeling requires the modeller to understand the relation and implementation that a variable has on an equation, in an effort to best “estimate” the function output to a certain error.
On the other hand, machine Learning requires minimal human effort, as the workload involved in computing is placed squarely on the machine. Furthermore, Machine Learning has a strong predictive power, as the machine is “fit” and “trained” to find patterns in the data.
| Machine Learning | Statistical Modeling | |
|---|---|---|
| Network, Graphs | Model | |
| Weights | Parameters | |
| Learning | Fitting | |
| Supervised Learning | Regression/Classification | |
| Unsupervised Learning | Density Estimation/Clustering |